- Compliance
- Compliance Regulations
- Security Compliance
- Federal Rules of Civil Procedures
- Sox Compliance
- Legal Compliance
- Basel II Compliance
- Pillars of Basel II
- Basel II Challenges and Solution Frame Work
- Operational Risk Management: Basel II Compliance
- The Importance of Compliance with CAPA system
- Best Practices for Increasing Information Security Compliance
- Asset Management
- Four Best Practices for Improving ER Results
- IT Data Security: ISO 17799
- Five Compliance Challenges for Insurers in 2012
- Compliance Best Practices
- Training and Development: Recommended Best Practices
- Agreeing to Administration
- SOX Compliance Essentials
- Application of the Basel II Accord for Compliance
- Latest Amendments in the Federal Rules of Civil Procedures
- Legal Compliance for Leading a Better Administration
- Securing Your Business with Best Practices
- Privacy and Personal Data: A Safe Flow of Information
- Advantages of Compliance Training
- Contract – Best Practices to Follow
- The Benefits of Compliance in Business
- The Importance of Compliance Training
- Regulatory Impact Analysis: Best Practices In OECD Countries
- War Regulations: 5 W Questions Answered
- Benefits of Regulatory Impact Analysis
- Compliance Management
- Compliance Officer
- Basel II Governance and Risk Manager
- Laying the Foundation
- Enterprise Quality and Compliance
- Compliance Management In 2011
- Dealing with Corporate Governance Issues in Asia
- SaaS Compliance Management
- Compliance Management System: An Overview
- Compliance with Payment Card Industry (PCI)
- Managing Security with Compliance Management
- How to Successfully Manage Suppliers and Ensure Safety and Compliance
- Security Compliance Management
- Commercial Business Realities and Government Compliance Requirements
- Need for Government Regulation in Business
- Four Best Practices for CIOs Ensuring Cloud Compliance
- Looking at Five Compliances In 2012
- Security Management
- Best Practices in IT Security
- Internet Security Best Practices
- Regulatory Compliance Management
- Six Compliance and Risk Management Challenges for Global Organizations
- Managing Compliance
- An Introduction to the Asian Issues of Corporate Governance
- Benefits of Practicing Good Corporate Governance Principles
- Duties of a Compliance Officer
- Financial Compliance
- Bank Compliance
- Advantages
- Foreign Account Tax Compliance – FATCA
- Sarbanes Oxley 404 Compliance Standards
- Regulation CC
- Financial Compliance Software
- Implementation of Value Added Tax (VAT)
- How to Balance a Budget
- Saving Your Company from Monetary Defiance
- Reviewing the Sarbanes-Oxley Act
- Sections of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act
- Tasks of a Bank Compliance Officer
- Budget Development through Best Practices
- Using Best Practices for Organizational Budgets
- Five Best Practices in Securing Investors
- Corporate Compliance
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Governance Guidelines
- Board Member Duties
- Email Archiving
- Directors Compliance
- IT Compliance
- Board Members Remuneration
- Procurement Compliance
- Requirements for Corporate Compliance
- Establishing an Effective Corporate Compliance Program
- Federal Government Requirements for Marketing
- The Vital Impact of Employment Law
- Acquisitions and Mergers – Changing Without Damage
- Best Practices in Procurement Compliance
- Laws and Regulations for Human Resources
- Top 10 Best Practices For HR
- Internationalization Best Practices: Simship
- Recovery Planning to Stay in Business
- Recommended Best Practices in HR Department
- Basics of Corporate Governance
- Golden Principles of Effective Corporate Governance
- Compliance: An Essential Tool for Success
- Best Practices for Investments in Africa
- Corporate Governance and Responsibilities
- Best Practice Guidelines for Recruitment and Selection
- Small Business Best Practice Benchmarks
- Maintaining Collective Deference
- Hiring a New Employee – Best Practice to Follow
- How to Conduct a Job Interview
- The Drawbacks of Corporate Governance
- The Essence of Corporate Governance
- The Key Principles of Corporate Governance
- Compliance Reporting
- Healthcare Compliance
- Health Care Compliance Association
- HHS OIG Compliance Program
- Fraud Risk
- Fraud Investigation
- Hazards Associated with Technology
- Purpose of Guidance for Healthcare Compliance
- Coding Component Is an Important Feature of Compliance Plan
- The Healthcare Laws Coming Up Soon
- Mitigating Risk of Employees’ Illness
- Benefits of Healthcare Programs in the Workplace
- Fitness and Conformity
- Corporate Health Issues
- Government Compliance
- Best Practices in Budget Management for Governments
- State Regulation on Budget Deficit
- Golden Rules: Making Balanced Budgets a Constitutional Obligation
- Government Information Compliance
- The Positive Consequences of Best Practices in Budget Balancing
- What Happens When Best Practices in Budget Balancing Are Not Respected
- Essential Governance Best Practices
- IT Governance Best Practices
- Best Practice in Budget Control
- Budget Development and Management within Departments
- Best Practices for Budgeting and Forecasting
- Planning for the Future
- Factors of Government Compliance
- An Introduction to Regulatory Impact Analysis
- Government Budgets
- 2010 Best Country budgets
- 2010 Worst Country Budget
- Formation of Government Budgets
- Ten Best Budgets of 2011
- A Look at Ten Best Budgets of 2009
- Five Important Traits of a Good Government Budget
- Top Ten Budgets of 2008
- Components of a Government Budget
- Ten Worst Budgets of 2008
- Ten Worst Budgets of 2009
- The Year 2011 in Review – 10 Worst Budgets
- Government Budget
- State Budgets
- Compliance Regulations
- Risk Management
- Risk Management Standards
- ISO 31000:2009 Risk Management – Principles and Guidelines
- ISO/IEC 27000
- COSO ERM 2004
- The OSHA Inspection
- ISO 31000 Risk Management
- Risk Management Standards (RMS)
- Following Risk Management Standards
- Best Practices Standards for Effective Risk Management
- Types of Inventory Risks
- Risk and Risk Management
- Project Risk Management
- Important Tips
- Risks vs. Issues
- Project Management: Risk Vs Issue
- Risk versus Issue Management
- Risk Vs Issue
- Not Taking the Plunge into Losses
- Risk Management – 4 Risks That Every Business Face
- Implementation Process for Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)
- The Process of Risk Management: Identifying Risks
- Best Practices in Sharing Data Online
- The Different Types of Risks That May Threaten Your Business
- Fundamentals of Risk Management
- Steps Required for Risk Management
- Financial Risks Faced by Banks
- Summary
- Risk Management Techniques
- Operational Risk Management
- Best Practices for Risk Management
- Risk Management Action Plan
- 5 Steps to Risk Management
- Introduction to Risk Management
- Looking at the Fundamentals of Risk Management
- Risk Management – Strategic and Operational Risks
- Types of Risk Management in Today’s Industrial Sphere
- Risk Decision
- Financial Risk Management
- Understanding Risk Management
- The Basics
- Business Risks
- Audit Risks
- Financial Investment
- GARP FRM Certificate
- SOX 404 TDRA
- ORM for Banks and Financial Institutions
- Policies for Financial Risk Management
- Credit Risk Management Overview
- Credit Rating and Risk Management
- The Important Role of Financial Risk Management
- Best Practice In Public Debt Management
- Sovereign Debt Risk Management
- Calculating Gear Ratio or Debt/ Capital Ratio
- Monitoring Credit Risks
- Scrutinizing Country Credit Risk
- Looking out for Your Finances
- Risk Management: Risk Control – Controllable and Uncontrollable Risks
- Small Businesses: Risks They Have to Fight
- Risk Assessment
- The Basics of Risk Assessment
- COSO IC – Integrated Framework
- Risk Management Strategies for Financial Institutions Using Social Media
- Security Audit Assessment
- Calculating Risk Assessment Values
- Evaluating Risk in Your Business
- Determining Your Liability
- Risk Management Process and Principles
- Goals and Techniques of Risk Management
- BS 25999
- Risk Control
- Risk Management Standards
- Regulation
- Bank Regulations
- Business Regulations
- The Need for Regulation
- Laws and Regulations for Business Best Practices
- The Successful Business Pattern
- A Path to Prosperity: Best Practices in Business Regulations
- Business Regulations: Essentials of a Valid Contract
- Starting and Running a Business Successfully
- Benefits of World Trade Organization’s Trading System
- Understanding The World Trade Organization’s Rules and Regulations
- Trade Regulations Landing Page
- 5 Businesses That Need Personal Behavioral Data
- US and the World Trade Organization
- Objectives For Regulatory Impact Analysis
- Financial Regulations
- General Objectives
- Fundraising
- Business Regulations
- Detecting Vulnerabilities in Regulations with Best Practices
- The Latest on Developments in Best Practice Regulations
- Preparing a Regulation Impact Statement (RIS) for Best Practices
- Financial Reforms of 2011
- Regulations Update for Best Practices in 2012
- Usury Regulations in the US
- 5 Challenges for Insurance Companies
- Understanding Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
- The Importance of Financial Regulations
- Financial Regulations – Introduction to IFRS
- Some Important Tips for Refinancing
- OECD Guidelines for Implementing Performance and Quality Regulations Effectively
- Why Trade Laws and Regulations are Important
- Regulatory Impact Analysis: Decision Making
- AIFMD
- Solvency II
- Sarbanes-Oxley Act
- Health and Safety Regulations
- Occupational Safety and Health Act
- Responsibilities of Employers
- 10 best practices in Value Analysis for Healthcare
- Health and Safety Commission (HSC) Regulations
- ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act) for Best Practices
- Challenges of Medical Device Regulations and 21 CFR Part II
- 4 Best Practices for Healthcare Marketers Using YouTube
- New Healthcare Regulations: 2012
- Impact of Regulation Best Practices on Social Media Healthcare
- Government Regulations on Pharma – Social Media
- Healthcare Regulations on Pharmaceutical Sales
- Healthcare Regulations in UAE
- Safety at Work: A Dominant Issue
- War Regulations: How Things Should Be
- Reporting
- The Accounting Process
- The Accounting Cycle
- 10 Important Accounting Terms
- Managing Cash Flow
- Top Trends for Small Accounting Firms
- The Payback Accounting Formula
- The Accounting Equation
- Keeping your Accounts Clear
- Managing Cash Flow with Minimum Input
- Hiring Investment Bankers for Safe Returns
- Financial Accounting – Requirements of IFRS
- Audit
- Valuation Best Practices
- What is the fair price of a private company?
- Best Practices for Customer Relationship Management
- Five Key Best Practices to Improve Your Customers’ Experience
- Best Practices in CRM via Social Networks
- Best Practices in Content Management for Social Networks
- Best Practices in Brand Management on Social Networks
- Why Businesses Choose LinkedIn
- 5 Simple Steps to Determine ROI via Social Media
- Five Best Practices for Businesses on Social Media
- How to Gauge Your Social Marketing Strategy
- Best Practices to Increase Speed and Performance of Your Business Website
- Best Practices in Public Affairs
- SEO Best Practices
- Business with Networks: Recommended Best Practices
- Valuation Best Practices: Using the Internet as your Apprentice
- Keeping a Close Watch on Consumer Privacy
- Best Practice – Facebook Privacy
- How to Inculcate Best Practices in Privacy
- Five Best Practices for Facebook Users
- War Crimes
- Sharing Data on Social Networking Sites: Best Practices to Follow
- Why You Should Not Neglect Terms of Services
- Performance Monitoring
- Performance calculations – Three levels of IRR
- Cost Control
- Crowd Sourcing Is a Best Practice
- A Guide with Best Practices for Indirect Costing
- Highly Effective Balance Sheet Reconciliation
- A Guide for Indirect Costing
- Best Practice in Monitoring Public Expenses
- Best Practices for Public Tenders
- Supervising Conduct for Best Practices
- Best Practices in Privacy: Duties of the Employer
- Performance Monitoring at a Glance
- Reporting: Employee Performance Management
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Behavioral Data Collection Techniques
- Collecting Behavioral Data – Quantitative Techniques
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Personal Data Collection
- How Online Behavioral Data Collection Works
- Collecting Behavioral Data Through Cookies
- Audit Committee Best Practices
- Audit Committees Fiduciary Duties
- Audit Committee Exposure to Liability
- Audit Committee Members Qualifications
- Principal Functions of the Audit Committee
- Quarterly Review and Discussion of Financial Statements and Disclosures
- External Audit Monitoring Best Practice
- Quarterly Review of Accounting Policy
- Risk of Fraudulent Reporting
- Conduct and Timing of Meetings
- Monitor the Company's Internal Audit Function
- Quarterly Review of the Adequacy of Internal Controls
- Assess the Audit Committee's Role
- Policies Regarding Notifications to Audit Committee
- Best Practices – Monitoring Accounting
- Audit Committee Charter and Proxy Statement Disclosures
- Advantages of Lean
- Best Practices in the Lending and Loan Administration
- Internal Audit and Good Governance
- Audit Committee Best Practices: An Insight
- Types of Accounting
- Best Practices in Accounting
- Generally Accepted Accounting Principles – GAAP
- International Financial Reporting Standards – IFRS
- Best Practices in Target Costing
- Financial Reporting for Best Practices in Accounting
- Accounting Hosting: A New Accounting Trend
- Importance of Financial Statements for Best Practice
- Best Practices for Accounts Payable
- Best Practice in Credit Rating
- An Important Accounting Term: “Accounting Cycle”
- Best Practices in Revenue Recognition
- Analysis of Net Present Value
- Three Crucial Accounting Terms
- Accounting Regulation in Emerging Capital Markets
- Starting an Accounts Department with Best Practices
- Best Practices for Hedge Accounting
- Reporting for Good
- Best Practice in Sovereign Debt
- A Cost Accountant Following Best Practices
- Accounting: Methods of Inventory Valuation
- Accounting: Various Types of Costs
- The Accounting Process
- Best Practice Software
- Compliance Software
- Regulatory Compliance Software
- Tax Compliance Software
- Email Archiving
- Regulations and Licensing
- List of Best Compliance Software Applications
- Financial Compliance Software
- Software Compliance: Computing and Auditing
- Policy Management Software Is Your Need
- Quality Compliance Software for Business Challenges
- SIIA Software Metering
- Best Practices for Software Testing
- Return of CRM Software
- HR Software to Ensure Regulation Compliance
- Best Practices for SOA Governance Software
- Safeguarding Your Ongoing Business Success and Efficiency
- Software Development for Better Business Management
- Best Practices to Ensure Successful Software Implementation
- Best Practices for Secure Software Development
- IT Software Industry Best Practices
- Secure Software Development: Some Rules to Follow
- Using Security Software: Best Practices to Follow
- Regulation Software
- Accounting Software
- Healthcare Software
- Risk Management Software
- Benefits
- For Banks
- How-to-Choose Guide
- Saving Your Business from Unpredictable Hazards
- Why Risk Management Software for Organizations
- The Role of Risk Management Software in Global Recession
- Things to Consider When Purchasing a Risk Management Software
- Risk Management Software – 5 Things to Remember When Buying
- Benefits of Using Security Software
- Businesses And Security Software
- Security Software Landing Page
- Types of Security Software and Their Main Uses
- Using Antivirus – Best Practice to Follow
- Compliance Software
- Governance
- Data Governance
- The World Rakes in All the Goods As the Dollar Begins to Steady Itself
- The Promise of the Big Data Era
- The Paradigm Shifts That Will Occur Because of Big Data
- The Age of the Big Data
- Prepping Big Data For Your Business: Focusing On Governance and Quality
- Leveraging Big Data For Search and Social Media
- Investors on the Prowl as US Federal Reserve Encourages Selloff
- Incorporating the Use of Intelligence for Big Data Security
- Identifying Data Governance Problems
- Facebook – Our Privacy and the Big Data Hype
- Ensuring the Success of Data Governance Practices
- Dow Jones Taking a Plummet as Stocks on Wall Street Slide
- Creating Value of Social Minutia With Big Data
- Big Data Reveals 4 Big Things about Facebook Users
- Big Data – It's Quality Not Quantity that Counts
- Big Data Means Big Business – Seeing Social Analytics into Action
- Big Data – Humanities Global Pulse
- Big Data Changing The Way We Travel
- Approaching GRC in a Strategic Manner
- An Insight into Data Governance
- A New Approach Required For the Big Data Security
- A Big Piece from the Big Data Privacy Cake
- Data Governance: Addressing the Essentials
- Using Big Data To Create Great Customer Experience
- Governance – Compliance
- Remember Export Compliance Goes Along With NDAs
- Knowing What to Do When Your Compliance Program Fails
- Financial Institutions Lead the Rest When it comes to Compliance and Risk Management
- Financial Compliance – Understanding The Nature of Compliance
- Creating Flexible Reporting Systems
- Confidentiality in the Workplace – Taking Classified Information To A Whole New Level
- Compliance – A Look into Risk Management
- Approaching and Understanding Ethics and Compliance Risk
- What is the Chinese Wall?
- Compliance Risk: What Would it be Like in the Future?
- Your Compliance Management Can Make All the Difference
- Governance – Risk Management
- The Benefits of a Risk Management Software
- Risk Assessment: A Look at the Steps Involved
- Profiling The Internal “Fraudster”
- Outlaws Beware Fraud Investigators Have Gone Social
- Managing Your Fraud Risk
- Internal Fraud Investigation – Assessing the Control Factors
- Identifying the Elements of Fraud
- Conflict of Interest in the Government
- Tips For Businesses to Prevent Fraud
- Understanding the Basics of Conflict of Interest
- Data Governance
-
Best Practice » Reporting » Best Practices in Accounting » Accounting: Various Types of Costs » Accounting: Various Types of Costs


 Accounting: Various Types of Costs
Accounting: Various Types of Costs
- Best Practices in Accounting -
- Generally Accepted Accounting Principles – GAAP
- International Financial Reporting Standards – IFRS
- Best Practices in Target Costing
- Financial Reporting for Best Practices in Accounting
- Accounting Hosting: A New Accounting Trend
- Importance of Financial Statements for Best Practice
- Best Practices for Accounts Payable
- Best Practice in Credit Rating
- An Important Accounting Term: “Accounting Cycle”
- Best Practices in Revenue Recognition
- Analysis of Net Present Value
- Three Crucial Accounting Terms
- Accounting Regulation in Emerging Capital Markets
- Starting an Accounts Department with Best Practices
- Best Practices for Hedge Accounting
- Reporting for Good
- Best Practice in Sovereign Debt
- A Cost Accountant Following Best Practices
- Accounting: Methods of Inventory Valuation
- Accounting: Various Types of Costs
- Good Quality Financial Reporting for Best Practices in Accounting
- Best Practices for Small Businesses with Online Accounting
- The Accounting Process +
- Audit
- The Accounting Cycle
- 10 Important Accounting Terms
- Managing Cash Flow
- Top Trends for Small Accounting Firms
- The Payback Accounting Formula
- The Accounting Equation
- Keeping your Accounts Clear
- Managing Cash Flow with Minimum Input
- Hiring Investment Bankers for Safe Returns
- Financial Accounting – Requirements of IFRS
- Ten Crucial Accounting Principles
- Types of Accounting +
- The U.S. Department of Labor’s Four Types of Accounting
- Cost Accounting
- Forensic Accounting
- An Introduction to Management Accounting
- Methods of Depreciation
- Valuation Best Practices +
- What is the fair price of a private company?
- Best Practices for Customer Relationship Management
- Five Key Best Practices to Improve Your Customers’ Experience
- Best Practices in CRM via Social Networks
- Best Practices in Content Management for Social Networks
- Best Practices in Brand Management on Social Networks
- Why Businesses Choose LinkedIn
- 5 Simple Steps to Determine ROI via Social Media
- Five Best Practices for Businesses on Social Media
- How to Gauge Your Social Marketing Strategy
- Best Practices to Increase Speed and Performance of Your Business Website
- Best Practices in Public Affairs
- SEO Best Practices
- Business with Networks: Recommended Best Practices
- Valuation Best Practices: Using the Internet as your Apprentice
- Keeping a Close Watch on Consumer Privacy
- Best Practice – Facebook Privacy
- How to Inculcate Best Practices in Privacy
- Five Best Practices for Facebook Users
- War Crimes
- Sharing Data on Social Networking Sites: Best Practices to Follow
- Why You Should Not Neglect Terms of Services
- War Crimes Against Children
- Performance Monitoring +
- Performance calculations – Three levels of IRR
- Cost Control
- Crowd Sourcing Is a Best Practice
- A Guide with Best Practices for Indirect Costing
- Highly Effective Balance Sheet Reconciliation
- A Guide for Indirect Costing
- Best Practice in Monitoring Public Expenses
- Best Practices for Public Tenders
- Supervising Conduct for Best Practices
- Best Practices in Privacy: Duties of the Employer
- Performance Monitoring at a Glance
- Reporting: Employee Performance Management
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Behavioral Data Collection Techniques
- Collecting Behavioral Data – Quantitative Techniques
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Personal Data Collection
- How Online Behavioral Data Collection Works
- Collecting Behavioral Data Through Cookies
- Monitoring and Accounting
- Not Quantity that Counts
- Audit Committee Best Practices +
- Audit Committees Fiduciary Duties
- Audit Committee Exposure to Liability
- Audit Committee Members Qualifications
- Principal Functions of the Audit Committee
- Quarterly Review and Discussion of Financial Statements and Disclosures
- External Audit Monitoring Best Practice
- Quarterly Review of Accounting Policy
- Risk of Fraudulent Reporting
- Conduct and Timing of Meetings
- Monitor the Company's Internal Audit Function
- Quarterly Review of the Adequacy of Internal Controls
- Assess the Audit Committee's Role
- Policies Regarding Notifications to Audit Committee
- Best Practices – Monitoring Accounting
- Audit Committee Charter and Proxy Statement Disclosures
- Advantages of Lean
- Best Practices in the Lending and Loan Administration
- Internal Audit and Good Governance
- Audit Committee Best Practices: An Insight
- Financial Reporting
- Internal Control
- Mean Auditing Machines
Cost accounting is an important part of accounting. For every business it is important to control costs, which is not possible until the business understands them well. There are many types of costs that differ from business to business. Understandably, the costs incurred increase as a business increases production. However, marginal cost (cost for each additional unit) may start declining if a business is able to achieve economies of scale.
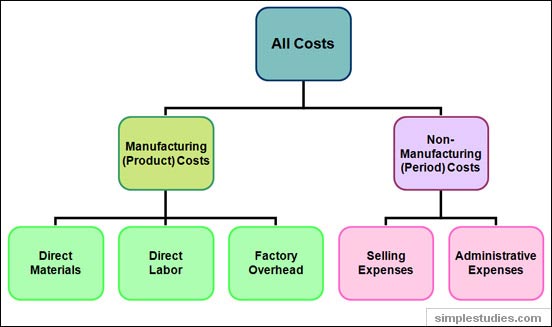 To understand the system better, explained below are some main types of costs:
To understand the system better, explained below are some main types of costs:
Fixed Costs
Fixed costs are the costs that are fixed and do not change with a change in production quantity. Some examples include; rent and manager’s salary. Understandably, rent would not increase if you increase production. However, it would increase if the production reaches a stage where you have to rent more space to accommodate the goods produced. At this stage it will turn into a semi-fixed cost.
Variable Costs
Variable costs, as the name suggests, are the costs that are directly linked with the output. These costs increase with an increase in output and vice versa. Some examples include raw material. If a business wishes to produce more goods it will have to buy more raw material that will result in its variable cost increasing. In the same way if it wishes to reduce production it will have to spend less on raw material that will result in its variable cost decreasing.
Opportunity Costs
The cost of choosing one thing and letting another go is known as opportunity cost. Technically, this cost does not exist as one does not have to pay anything, which is why accountants do not take this cost into consideration. However, economists and managerial accountants consider this cost when making business decisions.
The best practice is to take this cost into consideration as it gives a clearer picture and helps take correct decisions. For example, if you have an empty space with two options (1) to open a coaching center (2) to open a gym and you decide to open a gym, then the revenue you could’ve earned by opening a coaching center is your opportunity cost as you had to let it go to choose the other option.
Sunk Cost
Sunk cost is a cost that has been incurred and cannot be recovered, for example, paying for insurance in transit and the goods reaching the destination safely. The insurance cost is a sunk cost because it cannot be recovered even though it did not turn out to be very useful.
 In addition to all these costs, there are several other costs that are directly associated with running a business. They include; operational cost and manufacturing costs.
In addition to all these costs, there are several other costs that are directly associated with running a business. They include; operational cost and manufacturing costs.
However, the main problem is to identify the costs correctly so that decisions regarding opening, continuing or closing a business can be taken. Understandably, all these decisions depend on costs. A business must make sure to put the costs in the right category to avoid problems
Additionally, they should also be able to differentiate between costs and general expenditure as everything that a business incurs is not necessarily a cost that should be taken into consideration when managerial decisions are being taken.
Further reading: Corporate Governance | Audit | Performance Improvement
| Sitemap | Links | Copyright 2024 Best-Practice.com. All Rights Reserved. |
