2010 best country budgets
Author: Bernard-Louis Roques
This page has a list of the top 25 countries in budget best practice, ranked by Government Budget Surplus (+) or Deficit (-) over GDP (in %).
A government budget is made of two basic elements: revenues and expenses.
Revenues are derived primarily from taxes and asset sell-of.
Government expenses include spending , investment (such as infrastructure or research & development), social and welfare expenses.
| Country |
Budget surplus or deficit |
|
as a % of GDP |
|
| Norway |
10,6 |
| Qatar |
4,8 |
| Algeria |
4 |
| Bolivia |
3,71 |
| Brazil |
2,2 |
| Saudi Arabia |
1,9 |
| Estonia |
0,2 |
| Sweden |
0,2 |
| Chile |
-0,4 |
| Paraguay |
-0,4 |
| Peru |
-0,6 |
| Indonesia |
-0,62 |
| Luxembourg |
-1,1 |
| South Korea |
-1,1 |
| Switzerland |
-1,3 |
| Canada |
-2,1 |
| Rwanda |
-2,1 |
| Mexico |
-2,3 |
| China |
-2,5 |
| Finland |
-2,5 |
| Denmark |
-2,6 |
| Singapore |
-2,6 |
| Tunisia |
-2,6 |
| Bulgaria |
-3,1 |
| Taiwan |
-3,2 |
2010 worst country budgets
Author: Bernard-Louis Roques
This page has a list of the worst 25 countries in budget best practice, or “25 worst practice”, ranked by Government Budget Deficit over GDP (in %).
A government budget is made of two basic elements: revenues and expenses.
Revenues are derived primarily from taxes and asset sell-of.
Government expenses include spending , investment (such as infrastructure or research & development), social and welfare expenses.
| Country |
Budget deficit |
|
as a % of GDP |
|
| Ireland |
-31,3 |
| Botswana |
-10,7 |
| Greece |
-10,6 |
| United Kingdom |
-10,3 |
| United States |
-10,3 |
| Portugal |
-9,8 |
| Spain |
-9,3 |
| Tanzania |
-8,8 |
| Latvia |
-8,3 |
| Egypt |
-8,1 |
| Poland |
-7,8 |
| Slovakia |
-7,7 |
| Ghana |
-7,5 |
| France |
-7,1 |
| Namibia |
-7,1 |
| Lithuania |
-7 |
| Romania |
-6,9 |
| Kenya |
-6,4 |
| Pakistan |
-6,3 |
| Euro Area |
-6,2 |
| Slovenia |
-5,8 |
| Malaysia |
-5,6 |
| Ukraine |
-5,5 |
| India |
-5,1 |
| Netherlands |
-5,1 |
Formation of Government Budgets
Budgeting is process that takes place in almost every household that consists of individuals who earn money. The purpose for forming a budget is to save the maximum amount of money with little expenses. Budgeting is also done to analyze the expenses and returns taking place within the house, office or government industry. We may be used to forming budgets within a month or every six months, but the process of forming government budgets is much harder than that.
 Government budgets are formed in nearly every country in the world, some lasting for a year while for others it may last two years. In accordance to best practices, budgets formed by the government are forced to go through a thorough analysis before being finalized in the parliament.
Government budgets are formed in nearly every country in the world, some lasting for a year while for others it may last two years. In accordance to best practices, budgets formed by the government are forced to go through a thorough analysis before being finalized in the parliament.
It is important that the presented budget is favorable to all the members of the house. Otherwise, revisions will take place making the process even longer than it already is. Typically, a budget formed for the monetary expenses and revenues of a government takes several months to be drafted for presentation. This time may range anywhere from six to nine or even ten months.
The reason budgets consume so much time for development is that every aspect of the budget is completely and thoroughly examined making sure there’s no room left for mistakes. The people who have been charged with the responsibility of drafting a budget have to make several calculations. One of the main calculations is the subtraction of expenses from revenues. These values are taken from the revenues and expenses taking place within the last fiscal year.
 By calculating the total amounts of profits and losses occurring within the previous year, budget drafters can assess the results properly. These people will examine the areas where budget deficits have occurred and try introducing innovative cost figures. These figures will ensure that the unnecessary fiscal costs harming the economy are eliminated and a maximum number of funds are spent on areas that promise full returns.
By calculating the total amounts of profits and losses occurring within the previous year, budget drafters can assess the results properly. These people will examine the areas where budget deficits have occurred and try introducing innovative cost figures. These figures will ensure that the unnecessary fiscal costs harming the economy are eliminated and a maximum number of funds are spent on areas that promise full returns.
Any projects that have been funded by previous budgets and are not yielding any benefits are going to be removed from the development list. Efforts for gathering funds can also be made if the project serves a prosperous purpose for the country’s economy.
Once a budget has been formed, it is introduced in the legislative for approval. There, different politicians and lawmakers will study the prospects and offer their content or discontent with the budget. If the budget is accepted by the majority of the legislation than it can be passed, otherwise it will have to be redrafted.
Ten Best Budgets of 2011
A government budget is basically an estimate of a country’s expenditures and incomes. It is passed by the legislature and agreed by the head of the nation.
Best practices say that a budget should always be prepared with care keeping it in a surplus (revenues>expenditure).
2011 saw countries recovering after the slump that started in 2008. Many countries were able to achieve a surplus budget thanks to their faith and commitment.
Mentioned below are ten best budgets of 2011. The list is compared seeing if the budget was in surplus or deficit.
1. Norway
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: 12.5
Norway retains the Numero-Uno position for the fact that its budget is always prepared with care. The country always rises up to the occasion balancing its budget well.
 2. Hungary
2. Hungary
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: 4
Hungary enters the chart at number two as one of the strongest economies after the recession phase. Country’s growth is tremendous mainly due to the efforts to concentrate on development.
 3. South Korea
3. South Korea
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: 0.8
South Korea continues to dominate the region. A huge portion of its 2011 budget went to research, education and defense.
 4. Switzerland
4. Switzerland
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: 0.8
Switzerland recorded a Government Budget surplus equal to 0.40 percent of the country’s GDP in 2011, making it one of the strongest economies in Europe.
 5. Estonia
5. Estonia
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: 0.1
Estonia stands in the middle of the list at 0.1%. The country’s public debt totaled 6%, which is lowest in years.
 6. Sweden
6. Sweden
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: 0.1
Sweden continues to grow after the recent slump with the country managing a positive budget after a small gap.
7. Germany
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -1.2
Germany had the fourth highest budget in 2011 with 37,000 million USD deficits. Country’s exports saw a fall that made the country rethink its strategies and it came up with a strong budget for 2011 that is aimed towards making Germany strong once again.
 8. Luxembourg
8. Luxembourg
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -1.2
The country has announced its aim to return to a balanced budget by 2014. Its 2011 budget was also prepared keeping the future plans in mind. The country reduced costs on unnecessary expenditures so that it can continue to thrive and have a surplus budget.
 9. Finland
9. Finland
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -2
The country continued to have the same scenario as in 2010 recording the same numbers. However, a look at 2011 shows how the country is improving, and planning to get a better hold on its revenues and expenditures by 2012. The budget was aimed towards improving the import/export situation and providing more facilities to the people.
 10. Australia
10. Australia
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -3.3
Closing the chart is Australia with its budget that was purely transparent and aimed towards providing benefits to the people.
P.S: Some numbers are based on estimates
A Look at Ten Best Budgets of 2009
A budget is said to be good when it is in surplus. Every country needs to balance its BOP; however, most countries fail to do so and go under debt.
Overall, 2009 was a bad year for almost every country as revenues were down due to the economic slump. However, a few countries were still able to achieve surplus budget.
Highlighted below are the top ten budgets of 2009 for your understanding.
 1. Norway
1. Norway
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: 1.7
Inflation in the country reached 3.98% in 2009; however, Norway maintained its number one spot due to its budget standing at a surplus. Almost every country faced a financial crisis during the period, but Norway managed to escape it thanks to better planning. Additionally, being a huge oil exporter helped the country a lot.
 2. Switzerland
2. Switzerland
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: 1
The country was able to have a surplus budget due to various reasons. For starters, Switzerland does not have to spend heavy on defense unlike other countries, such as the US. Additionally, it is also often criticized for a lack of government expenditure on public welfare.
 3. Luxembourg
3. Luxembourg
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -0.9
Luxembourg faced a 5% budget deficit in 2009. Like many other countries in Europe, Luxembourg also suffered a huge blow due to recession; however, the damage was comparatively lesser. With a $40.7 billion GDP it continued to flourish.
 4. Sweden
4. Sweden
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -0.9
Sweden changed its policies to meet the changing times and had a deficit budget in 2009, which still looked better in comparison to other countries. All the changes resulted in the country making it to the list of top 10 countries with the highest GDP.
 5. Estonia
5. Estonia
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -2
Estonia had several problems with its budget in 2009. The plans continued to change with an increase in VAT and other taxes. The government also cut the expenses so that BOP could be balanced. This one point helped Estonia remain in good health and make it to this list.
 6. New Zealand
6. New Zealand
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -2.6
The budget concentrated on a lot of good things including education, social development, and research. It was highly concentrated towards making the future brighter.
 7. Finland
7. Finland
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -2.7
Finland has an egalitarian country that pays special attention to education and development. Its 2009 budget was also a step in the same direction. That year also saw some major tax changes and more money invested in research and development.
 8. Denmark
8. Denmark
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -2.8
Denmark is among the world’s strongest economies. The world saw a slump in 2009; however, Denmark’s exports remained rock steady helping the country make it to this list.
 9. Germany
9. Germany
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -3.2
Europe’s biggest economy had to approve of a deficit budget to meet standards and continue to improve. The budget was aimed towards balancing the economy and giving it a boost so that the country could once again get back on its feet.
 10. Australia
10. Australia
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -4.1
2009 turned out to be a tough year for the country with revenues falling rapidly. The government had to cut income tax in an attempt to boost the country’s status. Nevertheless, the budget continued to provide welfare to people in the form of home owner grants and increased payments to the states.
Five Important Traits of a Good Government Budget
Preparing a government budget is not a simple task. There are several complex issues involved in it that have to be taken care of.
 Many experts have given some important cannons of budget that have to be remembered when preparing a budget of any kind.
Many experts have given some important cannons of budget that have to be remembered when preparing a budget of any kind.
Countries especially have to be very careful because too much is on the line. To understand the procedure better, given below are a few good traits of a good government budget.
Elastic
The budget should always be elastic. Understandably, there comes times when one needs to rethink strategies and change figures. If the budget does not allow any changes, it will not be a good budget.
Based on the country, the budget document has to pass several acid tests before it reaches the president for the final approval. Legislature and experts make many changes to the budget so that it suits the requirements, which is why the budget has to be elastic and easily changeable.
Sanctioned
 A budget should only be made by those who are sanctioned to do so. Additionally, those sanctioned to make the budget must be competent and experienced enough to handle such a huge task.
A budget should only be made by those who are sanctioned to do so. Additionally, those sanctioned to make the budget must be competent and experienced enough to handle such a huge task.
Making a small mistake in the preparation of a budget plan can cause a heavy damage to the government and the country as a whole. Many countries have actually fallen due to poor budgeting. They end up in heavy debt and find it difficult to strive.
Equal and Rational
The budget should be planned carefully. When making a federal budget, experts have to make sure that they do not end up doing any injustice to states or sectors. The budget has to be divided carefully so that all the sectors of the economy can flourish.
Many countries make the mistake of concentrating on one pillar and neglecting others. This is a big blunder that can cost heavy. It is important that one concentrates on all the points and divide the revenues properly.
Researched
A budget should always be prepared after doing a good amount of research. Since a budget in most cases is based on expected numbers, it is important that the number (revenue and expenditure) are reached with a lot of care so that the closest possible estimates are achieved.
Surplus
One of the most important qualities of a good budget is that it should be in surplus. Unfortunately, most countries have deficit budgets these days mainly due to the poor general economy, falling revenues, and unnecessary expenditure.
Countries have to resort to various means to balance their BOP that results in them going under debt. It is important for every country to recount history’s lessons when preparing a budget and not to make the same mistake again.
In addition to the above mentioned points, all the budgets should be transparent and available to those who will be affected by it. Lastly, for a budget to be effective, it must be fully adapted and followed as closely as possible.
Top Ten Budgets of 2008
A government budget is a paper that is often passed by the parliament, and agreed by the president or chief executive. As per best practices, a budget is said to be good when it is in surplus i.e.: revenues are higher than expenditures.
Mentioned below are ten best budgets of 2008. The list is compared seeing if the budget was in surplus or deficit.

1. Norway
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: 19.1
The country with a huge number of international brands stands at number one with its budget leaving behind other countries’ budgets by a huge margin. The budget was cleverly made with the aim to improve living standard of the people while focusing on non oil deficit.

2. Finland
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: 4.2
2008 saw Finland increase funding in research and development. The Finnish government readily approved the budget that was prepared to improve the people’s standard of living while concentrating on other areas as well.

3. Denmark
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: 3.3
Denmark continued to have surplus budget in 2008 despite the beginning of a tough period. The new budget surprised many as billions were awarded to R&D. The main aim was to keep the country at the top of the globalization wave.

4. South Korea
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: 3
South Korea has to devote a huge portion of its budget to defense expenditure due to its not-so-friendly relationship with a few countries. In 2008, it opened to foreign investment and exports during this period that helped it continue its growth.

5. Luxembourg
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: 3
Luxembourg is a small country that mainly flourishes due to its enviable geographical location. It thrives due to highly motivated workforce and innovation. Additionally, it is able to get the right budget as it does not have to invest a lot in defense expenditure and most of the budget is aimed towards development.

6. Switzerland
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: 2.3
In 2008, Switzerland stood at number 2 (behind Norway) in Europe. However, its budget was once again criticized by many as it failed to help the falling real income of the nation.

7. Sweden
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: 2.2
The government set out the direction of the economic policy concentrating on the right points. Keeping with best practices, its budget was elastic that allowed changes as suggested by the parliament.

8. Australia
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: 0.5
Australia’s 2008 budget had particular emphasis on family welfare. There were tax cuts in addition to huge amount being devoted to education and health sector. The tax plan was prepared very intelligently so that only high income earners would get affected.
 9. Netherlands
9. Netherlands
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: 0.5
Netherland suffered a blow in 2008 as recession hit in the last quarter. However, the country managed to meet its standards that were set in the budget.

10. New Zealand
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: 0.4
Winding up the list at number ten is New Zealand, a country that almost always makes it to the top 10 list. Its 2008 budget was aimed towards improving the country’s development while concentrating on education and health.
Components of a Government Budget
A government budget is basically divided in two main sections that are explained in detail below. However, it must be remembered that a budget is mainly based on estimates that are derived through research.
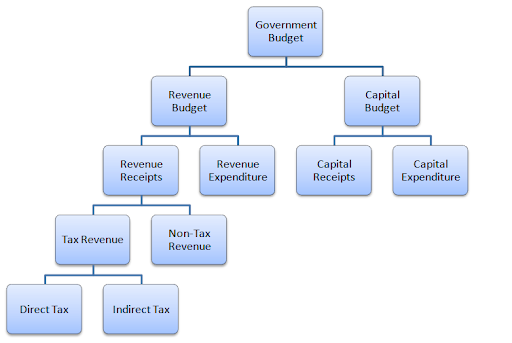 Revenues
Revenues
On one side are all the revenues that the government is expected to earn in the next twelve months. There are many sources of revenues.
Generally, they are divided under two sections:
Tax Revenues
Most of government’s revenue comes from taxes of various kinds. The 2012 figures estimate the government to receive $2.45 trillion in tax revenues. This section may be further divided into different types of taxes including “direct taxes” and “indirect taxes”.
Direct taxes are the taxes that have to be paid directly by the person they fall on. Whereas, indirect taxes are the taxes the burden of which can be passed along to others, such as general sales tax, which can be forwarded to customers as high prices.
Non Tax Revenues
On the other side, there are various other non tax revenues. Government receives interest on loans it has given to institutions. It is counted as revenue and added under this heading. Additionally, revenue earned from selling goods (land etc.) is also counted.
In addition to all these, the government also provides various services to different sectors. All the revenues earned through these services are also brought into consideration while preparing a government budget.
Expenditure
All the governments try to achieve a surplus budget i.e.: expenditure lower than revenues. However, the US government always has troubles doing so due to its huge expenditure.
Some main expenditure categories include.
Defense Expenditure
The US has to spend trillions of dollars on defense expenditure, mainly due to the fact that it is not on very friendly terms with a lot of countries and has to fund its armed forces deployed in several nations fighting terrorists.
In 2011, around $950 billion were spent in defense expenditure including veteran expenses and Department of Defense.
Welfare
A government budget has a huge impact on the population. The government has to make sure that people receive basic necessities of life, such as food, shelter, and healthcare. A lot of people in the US are deprived of such basic necessities for which the US government has to spend a huge chunk of revenue.
In addition to these, there are other categories, such as Social Security, which is an insurance program that is aimed to help old age, disabled and survivors.
Growth and Development
Natural disasters, mainly hurricanes are common in America. It has to spend a huge amount of money on rebuilding the economy that is destroyed by such natural disasters. In most of the cases, these disasters are unexpected, due to which the budget is not able to take them into consideration and the government has to resort to other means to fulfill the needs.
In addition to these there are several other categories, such as (Imports minus Exports, Interest etc).
Ten Worst Budgets of 2008
2008 was a bad year for almost every country as the economic slump started in 2008 and revenues started falling. Europe was among the most poorly hit regions with most European countries having a budget deficit in 2008.
Highlighted below are ten worst budgets of 2008.
 1. Iceland
1. Iceland
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -13.5
In 2008 headlines like “Iceland Goes Bankrupt” were regularly doing the rounds due to the financial crisis the country was going through. The sad phase reflected in its budget as well, as the country was not able to maintain its revenues. Many companies and banks, including the Glitnir bank were nationalized during this period.
 2. Greece
2. Greece
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -9.9
Greece was expecting a deficit, but not as wide as it ended up having. The country had been having trouble meeting standards set by the EU. Recession had affected social security and tax revenues resulting in lower than expected overall revenue that reflected in its budget.
 3. Ireland
3. Ireland
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -7.3
2008 saw Ireland’s first carbon budget. Ireland’s economy had started falling in 2007 with 2008 breaking the camel’s back, as revenues fell lower than expected. Some tax changes were made to give the economy a new lease of life; however, nothing worked as Ireland wrapped up the year with a huge deficit.
 4. United States
4. United States
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -6.6
Every kind of expenditure, from Medicare to defense to social security was increased in 2008; however, like any other year, revenues fell short that resulted in the US having a huge deficit of 6.6%. Most of its revenue was generated through tax sources including income tax and corporate tax.
 5. United Kingdom
5. United Kingdom
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -5
The UK was among the worst hit countries by the economic slump that started in 2008. UK’s 2008 budget was aimed towards balancing revenues while continuing to provide people with great services.
 6. Spain
6. Spain
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -4.5
Unemployment soared in Spain resulting in less revenue in income tax and more expenditure. The situation was totally opposite in 2007, which was a better year for the country that saw one of its worst financial years in 2008.
 7. Israel
7. Israel
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -3.8
The educational reform and military expenses soaked most of Israel’s budget in 2008 resulting in Israel having a huge deficit.
 8. Hungary
8. Hungary
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -3.7
Slow than expected growth poorly hit Hungary, like most other European countries. With falling revenues the government could not do much but have a negative budget.
 9. Poland
9. Poland
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -3.7
Poland’s 2008 budget was prepared after huge surveys so that the country could prepare for the worst. A huge chunk of revenue was spent in social security, justice, education and healthcare.
 10. Portugal
10. Portugal
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -3.7
Portugal was warned for its budget deficit as things were not looking to change in the near future. The country prepared a budget that was planned to bring it down to 3% or lower (EU’s requirement) however, experts believed that the country could not control its expenses better and carried huge risks.
Ten Worst Budgets of 2009
With the economic slump continuing in 2009, most countries found it difficult to balance their BOP or have a surplus budget. The top 10 list saw entrance of some new names as some maintained their not so desirable position from the previous year.
Highlighted below are ten countries with worst budgets in 2009.
 Ireland
Ireland
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -14.2
Ireland’s budget deficit almost doubled in 2009, as compared to the previous year. The country found it difficult to balance things or meet standards set by the EU as revenues started to fall with expenses continuing to go up.
 Greece
Greece
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -15.8
Greece’s situation continued to worsen with its deficit falling to almost 16%. With growing unemployment, revenues from multiple sources continued to fall.
 United States
United States
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -11.6
2009 was a very bad year for the US that could not reduce its expenditure due to its position. It continued to spend heavily on defense and welfare resulting in a huge deficit.
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -11
UK’s condition worsened as the country started looking for better options. With unemployment hitting all time low, the country started to work on law and order situation and a huge chunk of income was apportioned towards such expenses.
 Iceland
Iceland
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -10
Iceland’s trick paid off as the country improved in comparison to the previous years, falling from number one spot to number 5th spot, even reducing the overall deficit. The exchange rate stabilized in the last quarter of 2009 helping the country strengthen its position. However, inflation reached a record 18.6%.
 Portugal
Portugal
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -10.2
2009 did not bring any good news for Portugal that found it extremely difficult to balance things and have a surplus budget. The authorities promised to improve the situation in a few years by controlling expenses and finding ways to increase revenue.
 Spain
Spain
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -11.2
With an increased public deficit, Spain ended up having a huge budget deficit. The government took some major steps to control the alarming rate of unemployment, which resulted in falling revenues and increase expenses.
 Poland
Poland
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -7.4
The global financial crisis put Poland in a very weak position as its economy continued to fall down in 2009.
 Japan
Japan
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -8.7
Japan’s economy largely depends on its large-budget exports that fell largely with people not having the power to buy products like vehicles. Additionally, natural disasters that hit the country in the middle of 2009 resulted in huge expenses and the country having a budget deficit.
 Slovak Republic
Slovak Republic
General Government Deficit or Surplus as % of GDP: -8
Slovak Republic did not see favorable news in 2009 as its revenues sharply fell due to the economic crisis. However, the government came up with a strong budget, even though in deficit, to control the situations and promised to even things up within a few years.
In this section we will discuss:
- 2010 Best Country budgets
- 2010 Worst Country Budget
- Formation of Government Budgets
- Ten Best Budgets of 2011
- A Look at Ten Best Budgets of 2009
- Five Important Traits of a Good Government Budget
- Top Ten Budgets of 2008
- Components of a Government Budget
- Ten Worst Budgets of 2008
- Ten Worst Budgets of 2009
- The Year 2011 in Review – 10 Worst Budgets
- Government Budget
| Sitemap | Links | Copyright 2024 Best-Practice.com. All Rights Reserved. |

